이전에 코드에서 새로고침을 할 때 조회수가 증가하는 문제가 생겼다.
조회수 증가를 막아보자!
추가적으로 수정 시 현재 날짜를 반영하도록 구현해보자!
파일 목록
📦Board
┣ 📂board
┃┣ 📜list.html
┃ ┣ 📜modify.html
┃ ┣ 📜view.html
┃ ┗ 📜write.html
┣ 📂public
┃ ┗ 📂js
┃ ┃ ┣ 📜list.js
┃ ┃ ┣ 📜modify.js
┃ ┃ ┣ 📜view.js
┃ ┃ ┗ 📜write.js
┗ 📜index.html
구현
- view 페이지에서 새로고침을 할 때 조회수 증가 막기
- 수정 시 현재 날짜 반영
게시판 구현
게시판 구조

view 페이지에서 새로고침을 할 때 조회수 증가 막기
나는 새로고침 증가 시 조회수를 막기 위해 boards 데이터에 refresh라는 속성을 추가해 주었다.
# public/js/write.js
const writeFrm = document.querySelector("#writeFrm");
// 데이터 기본 틀
class Board {
constructor(indexNum, subjectStr, writerStr, contentStr) {
this.index = indexNum;
this.Subject = subjectStr;
this.Writer = writerStr;
this.Content = contentStr;
this.date = recordDate();
this.views = -1;
this.refresh = false; // 추가된 부분
}
// 값 설정시 빈 값 체크
set Subject(value) {
if (value.length === 0) throw new Error("제목을 입력해주세요.");
this.subject = value;
}
set Writer(value) {
if (value.length === 0) throw new Error("작성자를 입력해주세요.");
this.writer = value;
}
set Content(value) {
if (value.length === 0) throw new Error("내용을 입력해주세요.");
this.content = value;
}
}초기에 views속성을 처음에 -1로 설정해주고 refresh 속성을 false로 설정해주었다.
views 속성을 -1로 설정한 이유와 refresh 속성을 false로 설정한 이유는 view.js 코드에서 설명하겠다.
// 현재 날짜 반환 함수
const recordDate = () => {
const date = new Date();
const yyyy = date.getFullYear();
let mm = date.getMonth() + 1;
let dd = date.getDate();
mm = (mm > 9 ? "" : 0) + mm;
dd = (dd > 9 ? "" : 0) + dd;
const arr = [yyyy, mm, dd];
return arr.join("-");
};
// 글작성 버튼
const submitHandler = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const subject = e.target.subject.value;
const writer = e.target.writer.value;
const content = e.target.content.value;
try {
// boards 가져오기
const boardsObj = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("boards"));
// 객체 추가
const index = boardsObj.length;
const instance = new Board(index, subject, writer, content);
boardsObj.push(instance);
// boards 저장
const boardsStr = JSON.stringify(boardsObj);
localStorage.setItem("boards", boardsStr);
location.href = "/board/view.html?index=" + index;
} catch (e) {
// 예외 발생시 메시지 출력
alert(e.message);
console.error(e);
}
};
writeFrm.addEventListener("submit", submitHandler);# public/js/list.js
let boardsStr = localStorage.getItem("boards");
// localStorage 초기값 지정
if (boardsStr === null) {
const listStr = JSON.stringify([]);
localStorage.setItem("boards", listStr);
boardsStr = listStr;
}
const boardsObj = JSON.parse(boardsStr);
// 템플릿 생성
const template = (index, objValue) => {
return `
<tr>
<td>${index + 1}</td>
<td><a href="/board/view.html?index=${objValue.index}">${objValue.subject}</a></td>
<td>${objValue.writer}</td>
<td>${objValue.date}</td>
<td>${objValue.views}</td>
</tr>
`;
};
// 템플릿 반영
const tbody = document.querySelector("tbody");
for (let i = 0; i < boardsObj.length; i++) {
tbody.innerHTML += template(i, boardsObj[i]);
// 추가된 부분
boardsObj[i].refresh = false;
const refreshStr = JSON.stringify(boardsObj);
localStorage.setItem("boards", refreshStr);
}
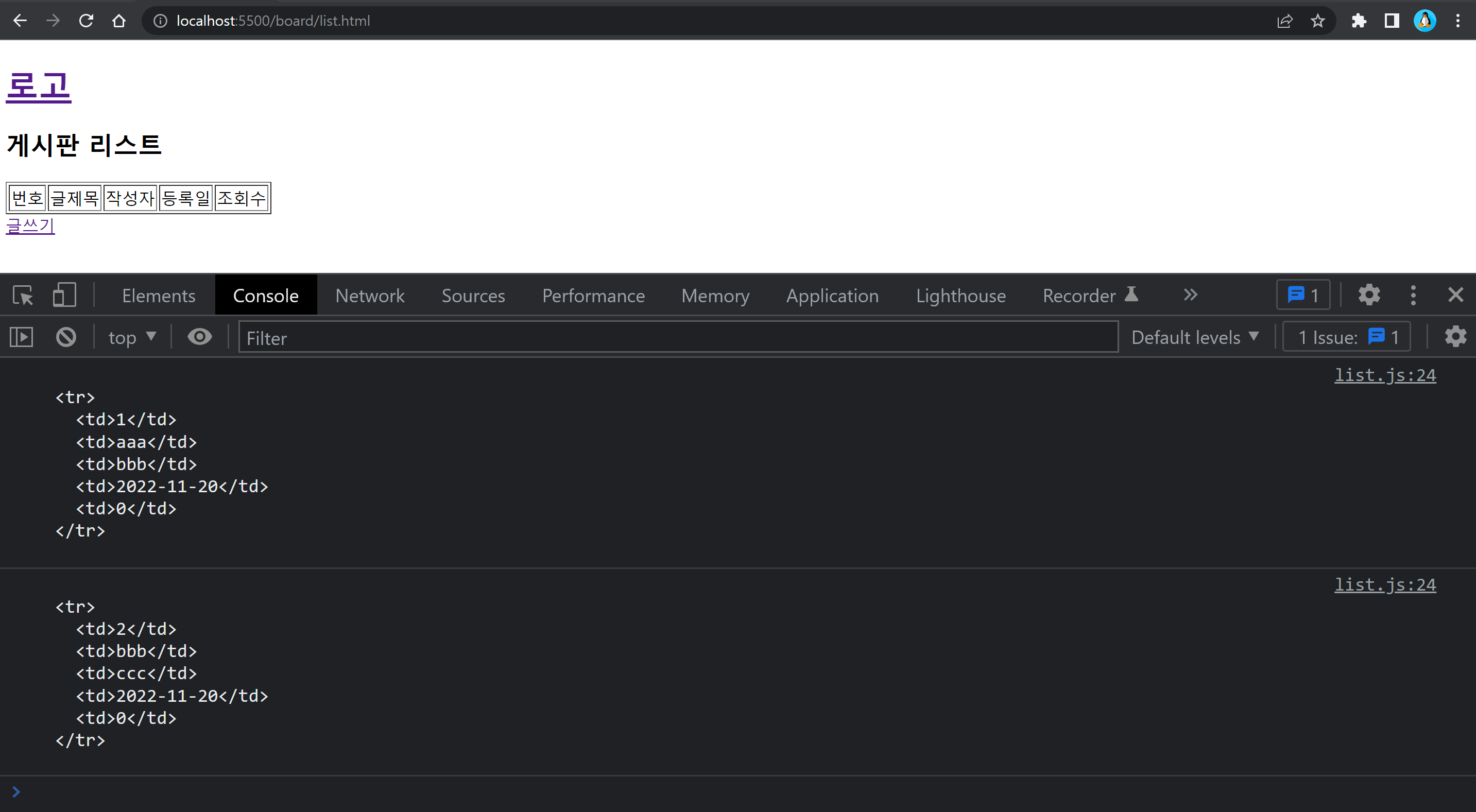
list 페이지에서 게시글 목록을 출력해줄 때 boards 객체의 refresh 속성을 모두 false로 바꿔서 localStorage에 반영을 해준다.
그 이유는 view.js 부분에서 설명하도록 하겠다.
# public/js/view.js
const boardsStr = localStorage.getItem("boards");
const boardsObj = JSON.parse(boardsStr);
const idx = location.search;
const index = idx.split("=")[1];
const board = boardsObj[index];
const beforeUrl = document.referrer;
// 조회수 수정된 부분
if (!board.refresh) {
board.views++;
board.refresh = true;
const viewCountStr = JSON.stringify(boardsObj);
localStorage.setItem("boards", viewCountStr);
} else {
if (beforeUrl === " ") {
board.views++;
const viewCountStr = JSON.stringify(boardsObj);
localStorage.setItem("boards", viewCountStr);
}
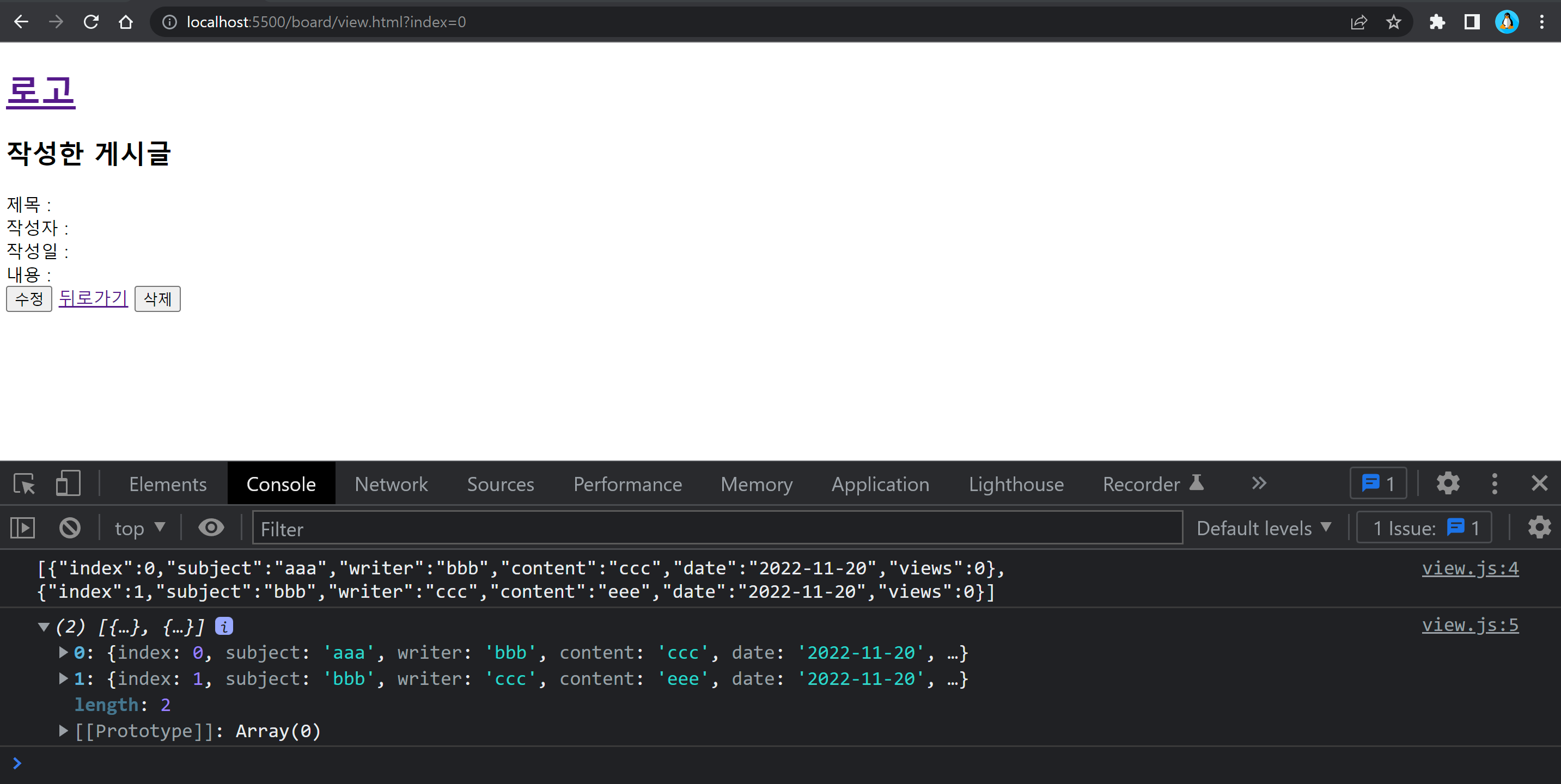
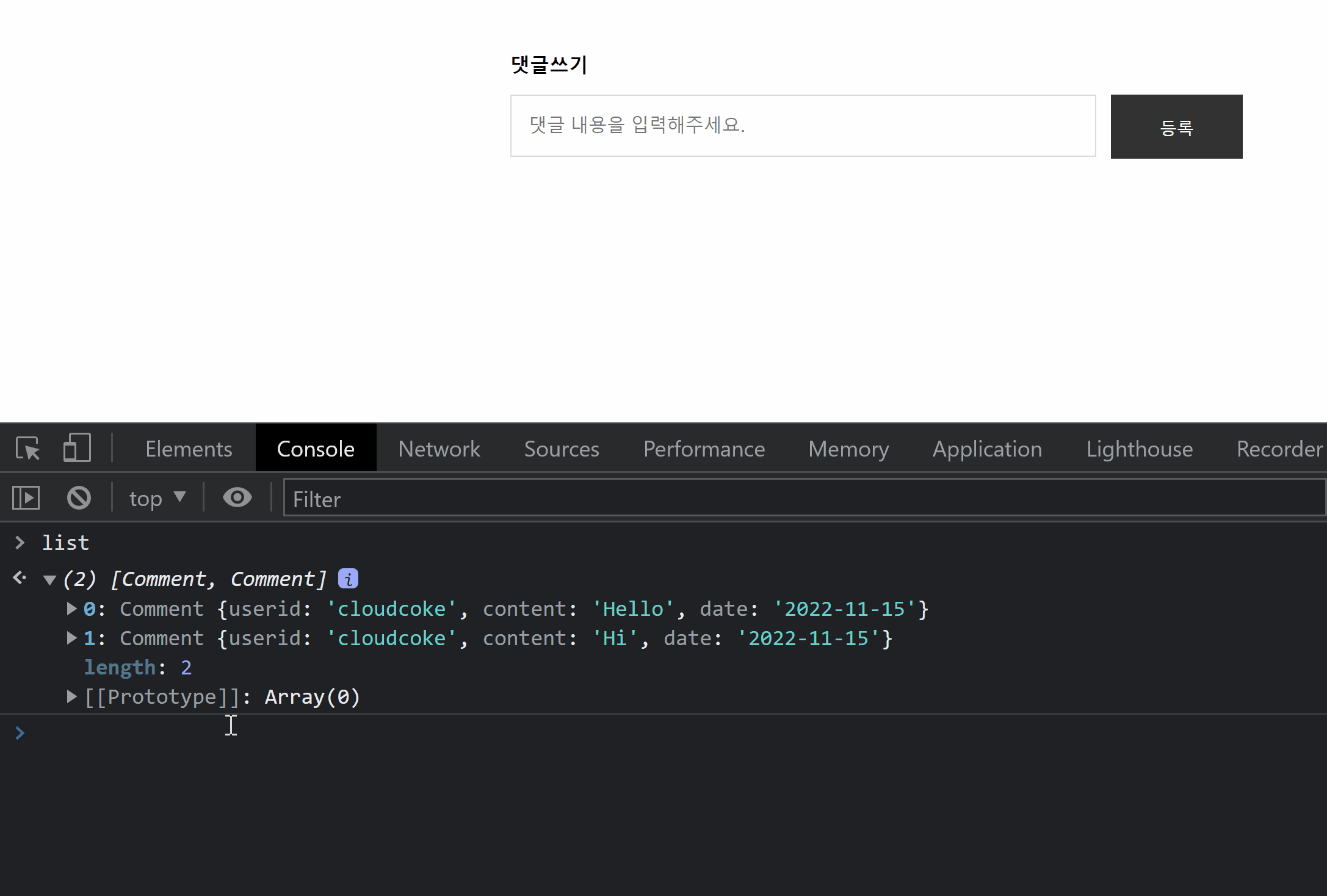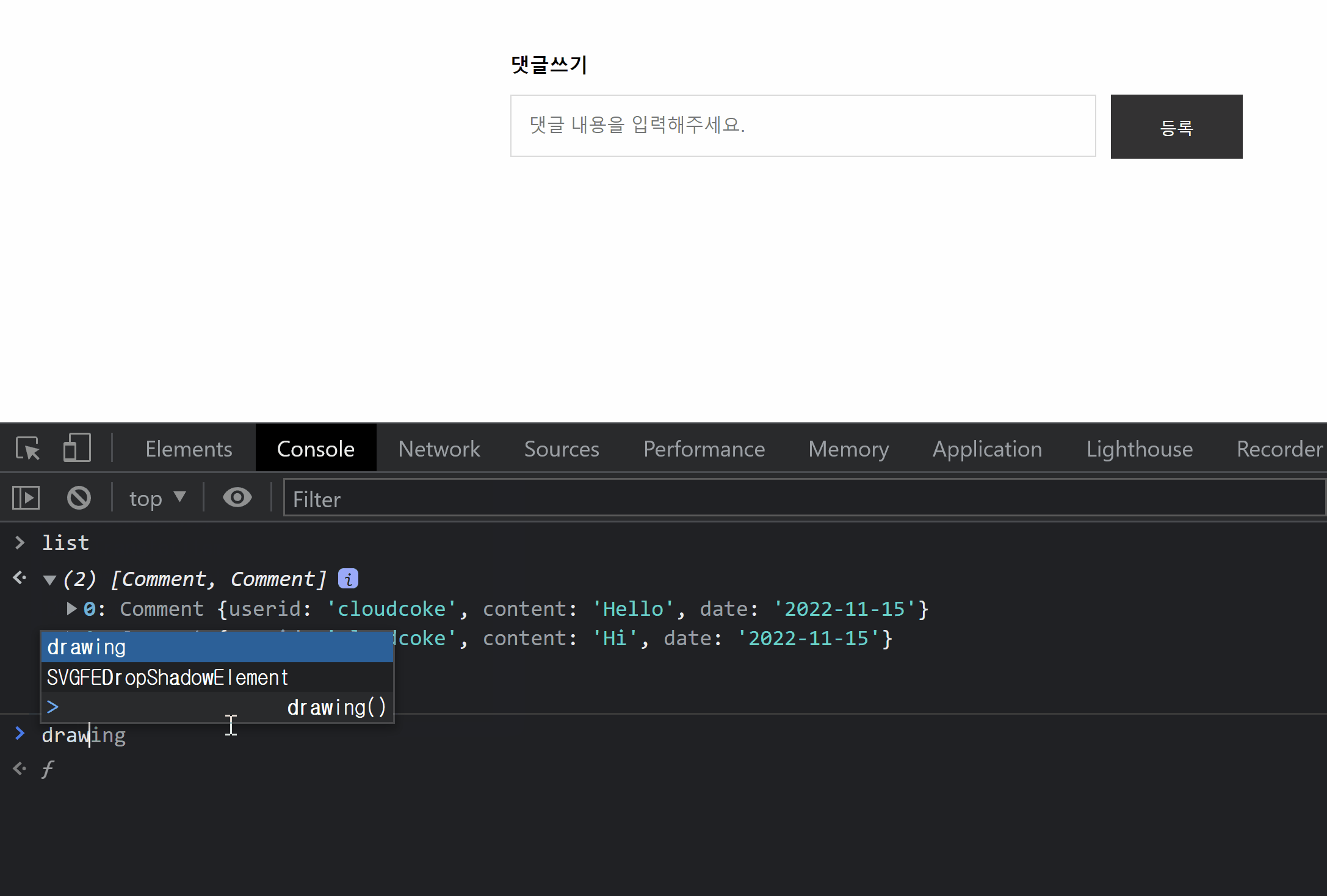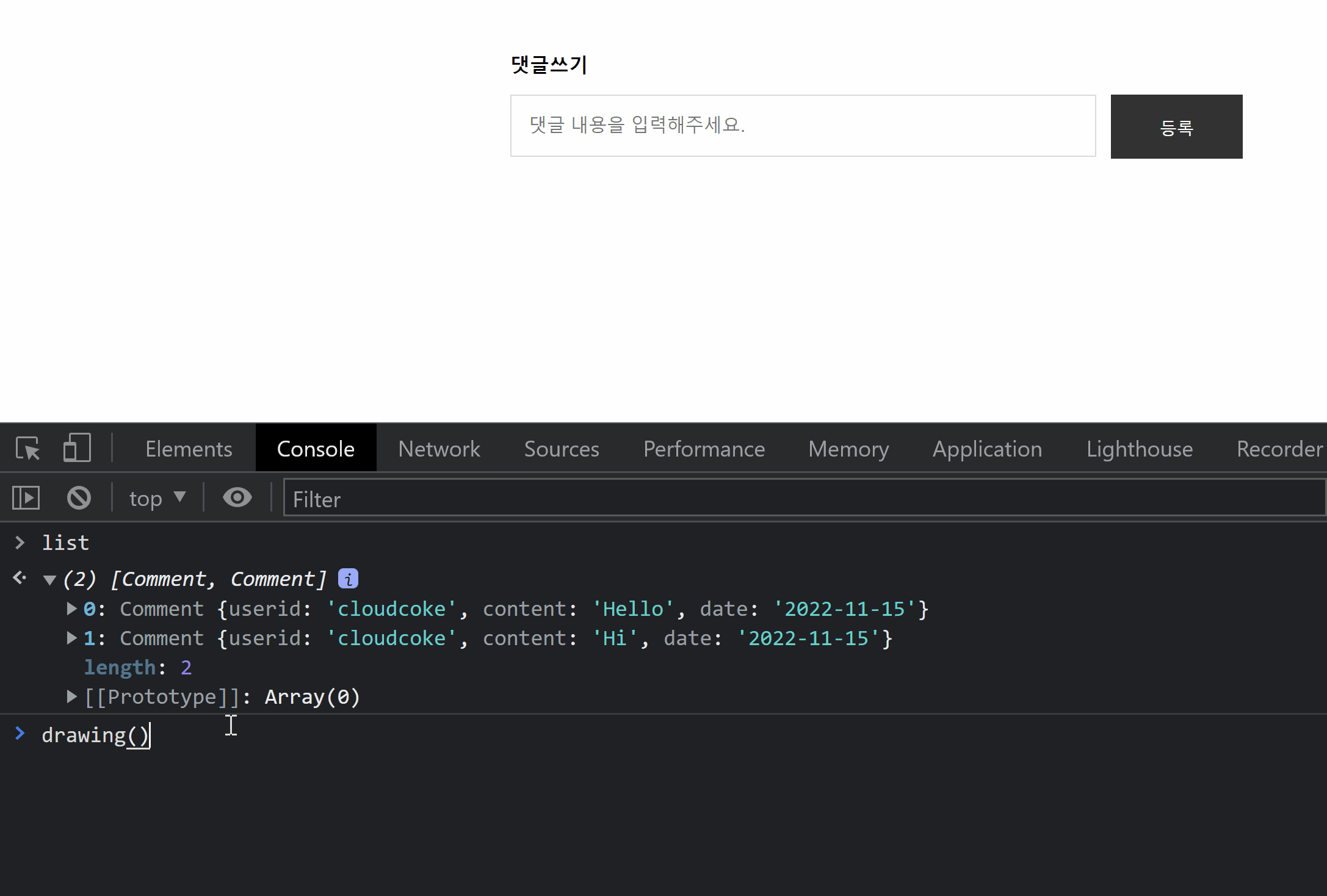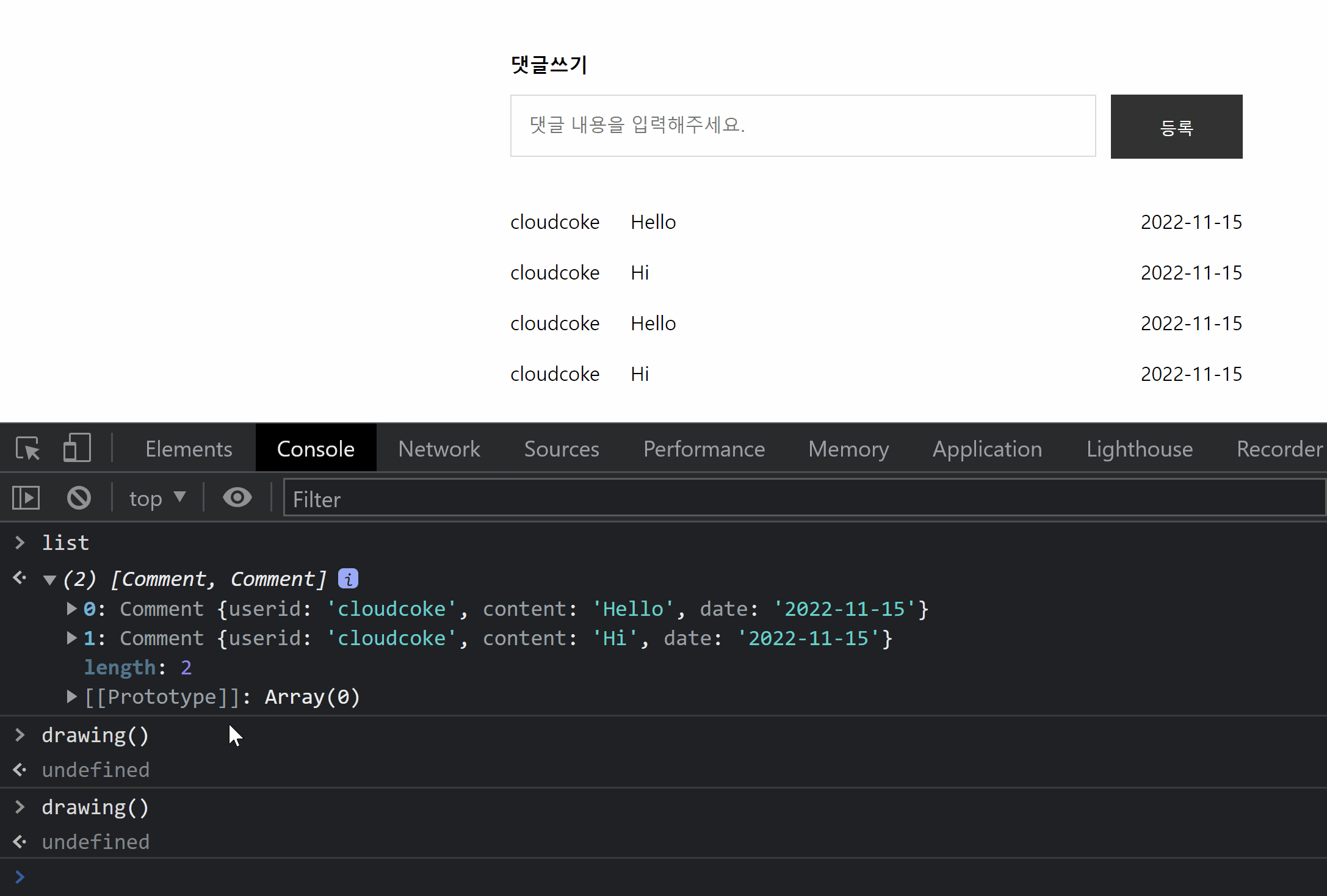
}만약 boards 데이터의 refresh가 false라면 조회수를 1 증가시키고 localStorage에 반영한다.
wirte.js에서 글을 작성하면 view 페이지로 넘어오게 되는데 이때 값이 1이 증가하게 되기 때문에 write.js에서 views의 초기값을 -1로 설정해주었다.
이렇게 하면 작성하고 view 페이지로 넘어오면 조회수가 0부터 시작한다.
만약 refresh 가 false라면 list 페이지에서 왔다고 보고 조회수를 1 증가시킨 뒤 boards 데이터의 refresh 속성을 true 바꾼다.
새로고침을 하게 되면 view.js 파일을 다시 로드하게 되는데 boards의 refresh 속성이 true이기 때문에 조회수가 증가하지 않는다.
예외로 이전 url이 빈 값인 url 즉 url에 직접 입력해서 들어온 경우 조회수를 1 증가시킨다.
이 경우에도 새로고침을 해도 조회수가 증가하지 않는다.
// 데이터 출력
const viewFrm = document.querySelectorAll("#viewFrm > div");
for (let i = 0; i < viewFrm.length; i++) {
const id = viewFrm[i].id;
viewFrm[i].innerHTML += " " + board[id];
}
// 수정 버튼
const modifyBtn = document.querySelector("#modify");
const modifyBtnHandler = (e) => {
location = "/board/modify.html" + idx;
};
modifyBtn.addEventListener("click", modifyBtnHandler);
// 삭제 버튼
const deleteBtn = document.querySelector("#delete");
const deleteBtnHandler = (e) => {
boardsObj.splice(index, 1);
for (let i = 0; i < boardsObj.length; i++) {
boardsObj[i].index = i;
}
const setBoardsStr = JSON.stringify(boardsObj);
localStorage.setItem("boards", setBoardsStr);
location.href = "/board/list.html";
};
deleteBtn.addEventListener("click", deleteBtnHandler);수정 시 현재 날짜 반영
const modifyFrm = document.querySelector("#modifyFrm");
const modifyFrmList = document.querySelectorAll("#modifyFrm > div");
const idx = location.search;
const index = location.search.split("=")[1];
const boardsObj = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("boards"));
const board = boardsObj[index];
// 게시글의 데이터 값 출력
for (let i = 0; i < modifyFrmList.length; i++) {
const element = modifyFrmList[i].childNodes[1];
const id = element.name;
element.value = board[id];
}
// 작성한 입력 값이 빈 값인지 검사
const isEmpty = (subject, writer, content) => {
if (subject.length === 0) throw new Error("제목을 입력해주세요");
if (writer.length === 0) throw new Error("작성자를 입력해주세요");
if (content.length === 0) throw new Error("내용을 입력해주세요");
};
// 현재 날짜 반환 함수
const recordDate = () => {
const date = new Date();
const yyyy = date.getFullYear();
let mm = date.getMonth() + 1;
let dd = date.getDate();
mm = (mm > 9 ? "" : 0) + mm;
dd = (dd > 9 ? "" : 0) + dd;
const arr = [yyyy, mm, dd];
return arr.join("-");
};이전에 write.js에서 사용한 현재 날짜를 반환해주는 함수인 recordDate를 사용하였다.
// 수정완료 버튼
const modifyHandler = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const subject = e.target.subject.value;
const writer = e.target.writer.value;
const content = e.target.content.value;
try {
isEmpty(subject, writer, content);
board.subject = subject;
board.writer = writer;
board.content = content;
board.date = recordDate();
const boardsStr = JSON.stringify(boardsObj);
localStorage.setItem("boards", boardsStr);
location.href = "/board/view.html" + idx;
} catch (e) {
alert(e.message);
console.error(e);
}
};수정 완료 버튼을 누르면 recordDate함수를 호출해 반환 값을 boards의 데이터에 덮어쓰도록 구현하였다.
const backBtn = document.querySelector("#back");
// 뒤로가기 버튼
const backBtnHandler = (e) => {
location.href = document.referrer;
};
modifyFrm.addEventListener("submit", modifyHandler);
backBtn.addEventListener("click", backBtnHandler);게시판 구경하기
최종 결과물 👈 클릭
'Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Javascript] 게시판 구현하기 (CRUD) - Delete (0) | 2022.11.21 |
|---|---|
| [Javascript] 게시판 구현하기 (CRUD) - Update (0) | 2022.11.21 |
| [Javascript] 게시판 구현하기 (CRUD) - Read (0) | 2022.11.20 |
| [Javascript] 게시판 구현하기 (CRUD) - Create (0) | 2022.11.19 |
| [Javascript] 댓글 구현하기 (Create, Read) (2) | 2022.11.16 |